What is data annotation?
Artificial Intelligence systems rely heavily on high quality data. This is because Machine Learning models learn through examples - lots and lots of them. These examples where objects are tagged with certain information to help Machine Learning systems learn, together form what is called a labeled dataset.
Essentially, data annotation is the process of labeling data to make it understandable and usable for Machine Learning models. This involves adding metadata to various forms of data such as images, text, audio, video or 3D, which helps algorithms learn and make accurate predictions.
The process of data annotation can be labor-intensive and requires attention to detail to ensure accuracy. Annotators need to understand the nuances of the data and the specific requirements of the model they are training. This often involves iterative feedback and refinement, where initial annotations are reviewed and adjusted based on the model's performance.
Effective data annotation is essential for the success of any machine learning project. It directly impacts the quality of the model's predictions and its ability to generalize from the training data to real-world scenarios. As such, investing in high-quality annotation practices and tools is crucial for developing robust and reliable AI systems.
Let us now have a look at 2D and 3D Data Annotations and understand them in more detail.
Difference between 2D and 3D data annotation
In the context of 2D and 3D data, annotation is crucial for training models that can recognize and interpret objects, patterns, and structures within that data. For 2D data, like images and videos, this might involve drawing bounding boxes or polygons around objects, tagging specific features, or identifying regions of interest. Annotators meticulously highlight these elements, providing the necessary context for the model to learn what each object looks like and how to identify it in future data.
3D data annotation, on the other hand, deals with point clouds and volumetric data captured by sensors like LiDAR. Here, annotators work with three-dimensional representations, marking objects and surfaces within the data. This can involve segmenting different parts of a scene, identifying objects within a space with cuboids, and ensuring that the model understands the spatial relationships between different elements. For example, in autonomous driving, 3D data annotation helps the vehicle understand its surroundings, recognize other vehicles, pedestrians, and obstacles, and navigate safely.
2D image innotation
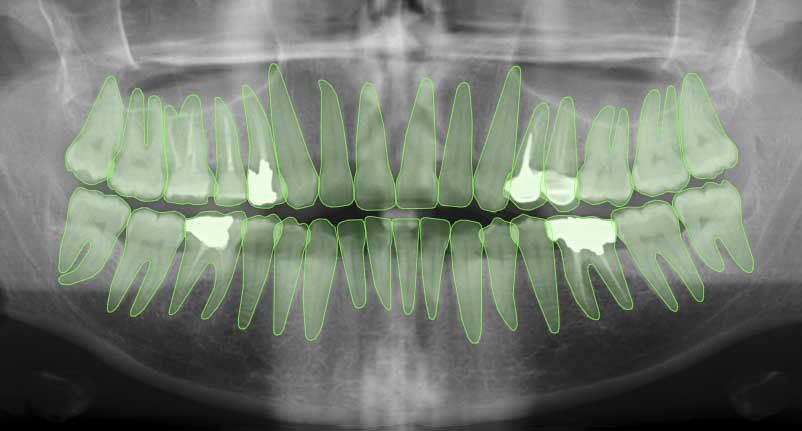
2D image annotation involves labeling images with relevant information to help algorithms learn to recognize and interpret visual elements. There are several common techniques used in 2D image annotation, including bounding boxes, segmentation, polylines & keypoints.
Bounding Box annotation
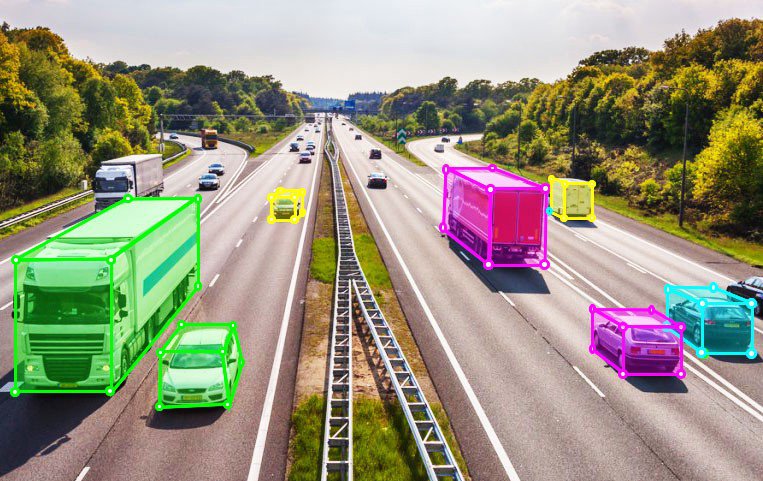
Bounding boxes are one of the most straightforward and widely used methods of image annotation. This technique involves drawing rectangular boxes around objects of interest within an image. Annotators manually outline each object, providing coordinates that specify the location and size of the box. These boxes serve as a reference for the machine learning model to identify and locate objects in new, unseen images. For example, in an image containing multiple cars, each car would have its own bounding box, helping the model learn to detect cars in various contexts.
Image Segmentation annotation
Segmentation takes the annotation process a step further by dividing an image into multiple segments, each representing a different object or region. Unlike bounding boxes, which only provide a rough outline, segmentation offers a more precise annotation by marking the exact boundaries of each object. There are two main types of segmentation: Semantic and Instance segmentation.
Semantic segmentation assigns a label to every pixel in an image, categorizing it as belonging to a particular object class (e.g., all pixels that make up a car). Instance segmentation, on the other hand, differentiates between individual instances of objects, even if they belong to the same class (e.g., distinguishing between two different cars in the same image). This level of detail is particularly useful in applications where precise object boundaries are necessary.
Polyline annotation
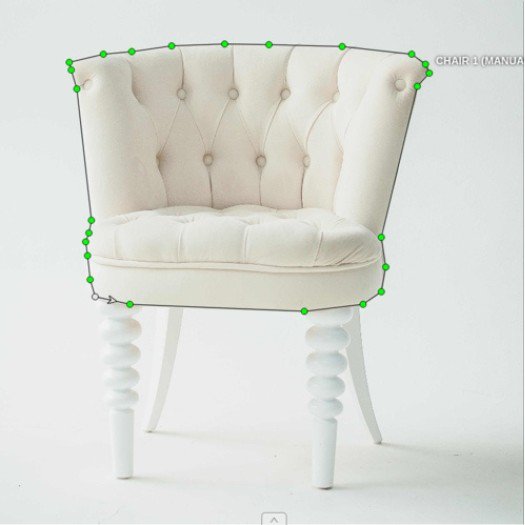
Polylines are used to annotate images by drawing lines that follow the contours of objects. This can be very useful for annotating linear features such as roads, railways, or edges of objects. Annotators create polylines by placing a series of points along the object's outline, which are then connected to form a continuous line. Polylines are essential in tasks like map creation, where accurate representation of pathways and boundaries is crucial. They provide a more detailed and accurate depiction of objects compared to bounding boxes, which may not capture the shape of elongated or irregular objects effectively.
Each of these annotation methods serves a specific purpose and provides different levels of detail and accuracy. Bounding boxes are ideal for quick and general object detection, segmentation is essential for tasks requiring precise object boundaries, and polylines are invaluable for linear and detailed annotations. Learn more about Polyline annotation here.
Keypoint annotation
Keypoint annotation involves identifying and marking critical features within images or videos. These keypoints serve as reference points that ML models use to understand and analyze the visual content.
For instance, in human pose estimation, keypoints are placed on joints such as elbows, knees, and shoulders. In facial recognition, keypoints might mark the eyes, nose, and mouth. By connecting these points, we can create a skeleton or a structure that represents the object’s shape and movement. Learn more about Key point annotation here.
3D cuboid labeling in 2D images
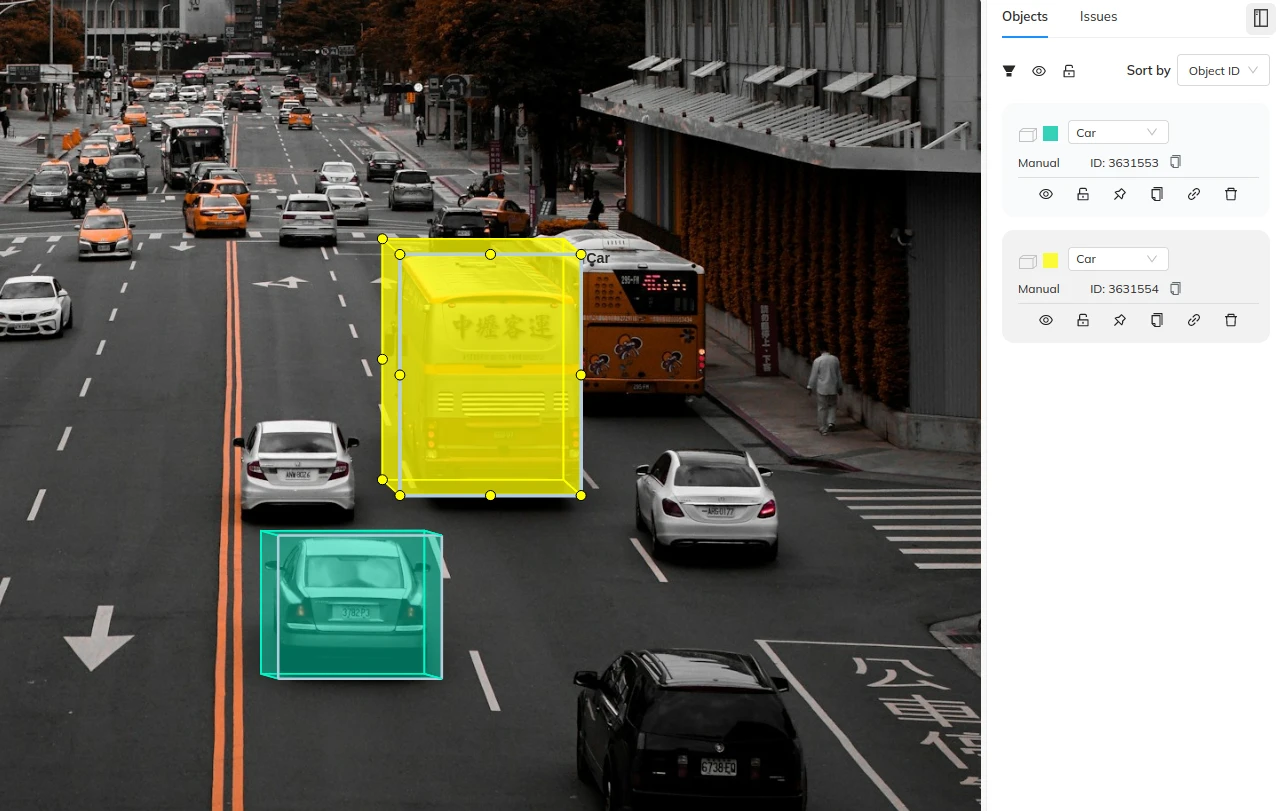
All the methods we talked about above, refer to labeling images with purely 2D shapes. Cuboid labeling, on the other hand, provides a three-dimensional perspective within a flat image. Unlike simple bounding boxes, which outline objects in 2D, cuboid labels offer a more detailed representation by marking the object's depth, width, and height. When annotators label an image with cuboids, they usually draw two boxes to define a cuboid - the front face and the back face of the cuboid. This additional sense of the object’s volume, helps Machine Learning models understand not just the position of the object but also its physical dimensions in the real world.
Cuboid labeling is particularly useful in applications like autonomous driving, where understanding the size and orientation of objects is essential for accurate distance estimation and navigation. Cuboid labeling is also beneficial in scenarios where objects are partially obscured or overlapping. By providing a more comprehensive annotation, cuboids help the model to better infer the spatial relationships between objects, even when parts of them are not visible. This results in more robust and reliable object detection and recognition in complex environments.
Common use cases of 2D image Annotation
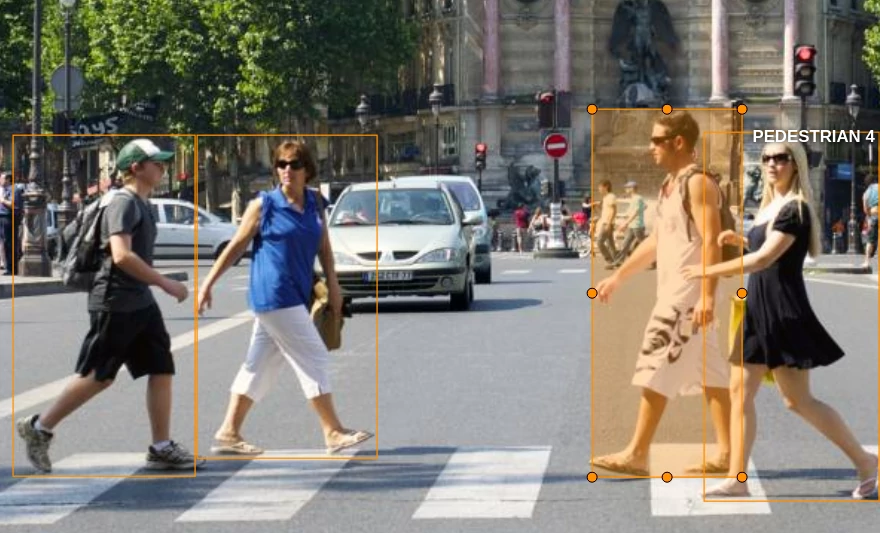
2D image annotation finds applications across a variety of fields. Here are some common use-cases where 2D image annotation plays a significant role.
Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on annotated images to understand and navigate their surroundings. Bounding boxes, segmentation, and polylines are used to label and identify other vehicles, pedestrians, traffic signs, and road markings. This detailed annotation helps the vehicle's AI systems to make decisions in real-time, ensuring safe and efficient navigation.
Medical Imaging
In healthcare, 2D image annotation is used to assist in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Annotators label medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to highlight areas of interest like tumors, fractures, or other abnormalities. This aids radiologists in their analysis and helps train models that can assist in early detection and diagnosis, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Retail and E-commerce
Retail and e-commerce platforms use 2D image annotation to enhance the shopping experience. Annotating product images with detailed tags helps in better search and recommendation systems. For example, an annotated image of clothing can include labels for color, style, and fabric, making it easier for customers to find exactly what they're looking for.
Agriculture
In agriculture, annotated images are used to monitor crop health, detect pests, and assess yield. Drones capture images of fields, which are then annotated to identify specific crops, measure growth stages, and detect any signs of disease or pest infestation. This data helps farmers make informed decisions about crop management and optimize their practices for better productivity.
Security and Surveillance
Security systems utilize 2D image annotation to enhance the accuracy of surveillance and monitoring. Annotated images help in identifying and tracking individuals, recognizing suspicious activities, and analyzing crowd behavior. This is particularly useful in areas like airports, public events, and critical infrastructure where maintaining security is paramount.
What is 3D data Annotation?
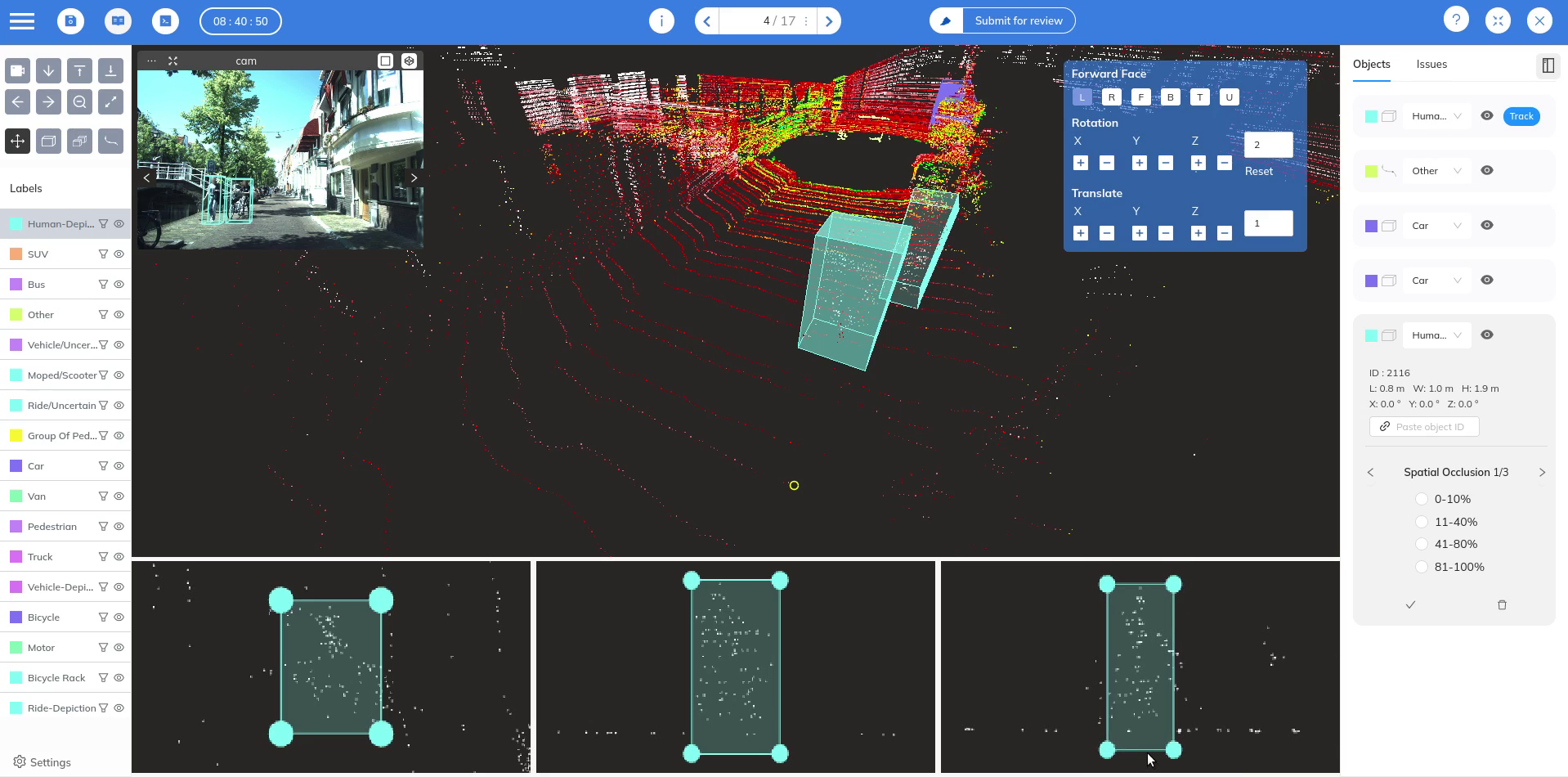
3D data annotation refers to annotating 3D data like point clouds and meshes.
Point clouds are a collection of points described by x, y, z co-ordinates, and are produced by various 3D scanning techniques like Lidars and photogrammetry.
A 3D mesh describes an object's surface by joining points in 3D space with polygonal shapes. 3D meshes are commonly used in the gaming and medical industry.
The two most prominently used labeling tools in 3D data labeling are Cuboid labeling and point cloud segmentation. We describe them below.
3D Cuboid Labeling
Cuboid labeling in 3D data involves annotating objects with three-dimensional boxes or cuboids. Compared with their 2D counter-points - that is - bounding boxes, 3D cuboids provide an even more accurate representation of an object's volume, orientation, and position in space. For example, annotators place cuboids around cars, pedestrians, and other objects captured by Lidar or depth cameras. This helps the machine learning model not just to detect these objects but also to understand their dimensions and how they occupy space relative to the sensor.
Point Cloud Segmentation
Point cloud segmentation is a technique used to label every data point in a point cloud that belongs to a particular class. Unlike 2D images, which are composed of pixels, point clouds consist of numerous data points that represent the surfaces of objects in three dimensions. Segmentation involves categorizing these points into different classes, such as buildings, trees, roads, and vehicles. Each point in the cloud is assigned a label, which helps the model to differentiate between various objects and understand their shapes and positions. Similar to image segmentation, point cloud can be segmented with semantic segmentation or instance segmentation methods.
Sensor Fusion Annotation
Sensor fusion annotation is another important aspect of 3D data annotation. It involves combining data from multiple sensors, such as cameras, Lidar, and radar, to create a comprehensive view of the environment. Annotators work with this fused data to provide detailed labels that take into account information from all sensors. For instance, a pedestrian detected by both a camera and LiDAR can be annotated more accurately by considering the data from both sources. This fusion enhances the model's ability to understand complex scenes and improves the robustness of object detection and classification.
3D data is particularly difficult to label because of the added dimension. In addition, Sensor fusion adds another layer of complexity as objects often need to be labeled consistently across sensors as well as time. A good data annotation platform can be the difference between a high quality labeled dataset and an inaccurately labeled one. The Mindkosh annotation platform allows you to easily label point clouds together with images. You can learn more about our 3D labeling platform here.
Conclusion
Data annotation, whether in 2D or 3D, is an essential component of many Machine learning applications. From bounding boxes and segmentation in 2D images to cuboid labeling and point cloud segmentation in 3D data, these techniques ensure that models can interpret and analyze visual information accurately. Sensor fusion annotation further enriches this process by integrating multiple data sources, leading to more reliable and detailed models. Understanding and implementing these annotation techniques is key to developing advanced systems that can navigate and make sense of the world around them. As these technologies continue to evolve, high-quality data annotation will remain a vital step in pushing the boundaries of what machines can achieve.




