Training reliable AI for autonomous vehicles, drones, and robotics rely heavily on high-quality annotated data. But unlike traditional computer vision datasets, these systems don’t rely on data from a single sensor. Instead, they capture the world through LiDAR, multi-camera video, radar, and other inputs simultaneously — each providing a unique perspective.
This is where Sensor Fusion annotation comes in. By labeling data across multiple modalities together, teams can build AI that not only “sees” but truly understands complex real-world environments.
But here’s the challenge:
- LiDAR produces millions of 3D points.
- Cameras deliver multiple video streams.
- Depth and thermal images complement RGB images..
- All of this needs to be annotated in sync, with consistent object IDs and appropriate context.
Not every labeling tool is designed to handle this complexity. Let’s break down the best sensor fusion annotation platforms available in 2025 - their strengths, weaknesses, and how to choose the right one.
What is sensor fusion annotation?
Sensor fusion annotation means labeling data from multiple sensors together to create a unified ground-truth dataset. For example:
- Drawing a 3D cuboid in LiDAR and projecting it onto camera feeds to enrich context.
- Labeling a vehicle across LiDAR, radar, and multi-camera views across time with the same ID.
- Segmenting LiDAR point clouds and identifying the corresponding cuboid in point clouds or objects in 2d images.
This ensures that downstream AI models can handle real-world tasks like lane detection, pedestrian recognition, and obstacle avoidance more reliably.
Key evaluation criteria
When comparing tools, here are the must-have capabilities for sensor fusion workflows:
- Sensor Coverage – Does it support LiDAR, radar, and multi-camera streams?
- 3D Visualization – Can annotations be viewed and edited in 3D environments?
- Projection Support – Can LiDAR annotations be projected onto 2D camera feeds?
- Object Tracking – Does it maintain consistent object IDs across time and sensors?
- Annotation Workflow and QA - Does it allow setting your own annotation workflows, and does it offer QA tools?
- Automation & Shortcuts – Features like interpolation, 1-click cuboids, or smart segmentation.
- Export Formats – Compatibility with AV/robotics standards for downstream use.
- Scalability – Can it handle large datasets and teams?
Mindkosh – Purpose-built for multi-sensor workflows
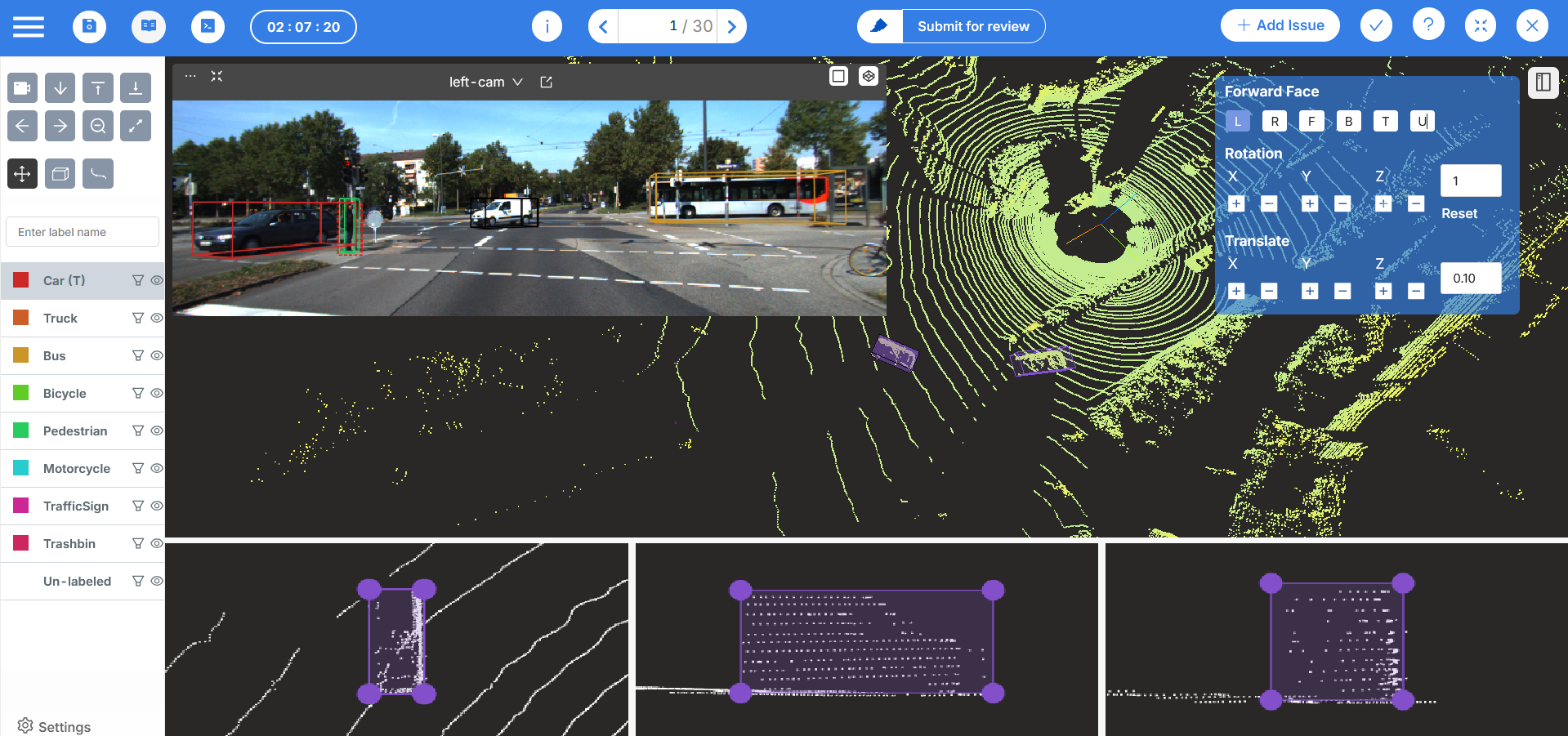
Unlike generalist platforms, Mindkosh is designed specifically for autonomous vehicles, robotics and Industrial automation use-cases. We offer native support for Point cloud annotation, Lidar Sensor fusion annotation, Mutiple camera image (Like Depth and Thermal) annotation and automation features that reduce manual work.
To try out Mindkosh yourself, simply create an account here and give it a go !
- Supported sensors - Mindkosh supports large Lidar/RADAR point clouds, RGB camera images and Single channel Depth/Thermal images, with ability to choose colormaps and merge multiple images together to provide additional context.
- Sensor Fusion – Annotate LiDAR and camera data together with consistent object IDs.
- 3D Visualization – Project annotations from Lidar to camera images in real time.
- Object Tracking – Track objects across time and sensors with consistent IDs and tools to ensure dimension consistency.
- Automation – Mindkosh offers 1-click annotation to quickly label cuboids. To reduce labeling time for segmentation, Mindkosh allows you to convert cuboids to segmentation. Intermediate and Forward Interpolation reduce labeling time for tracking objects across frames.
- Export Formats – Export annotations in Mindkosh format, following KITTI conventions. Conversion to other formats available through SDK. In addition, you can maintain different versions of the exported annotations and download them anytime.
- Annotation workflows - Setup a workflow that suits your needs, and easily perform Quality checking using Honeypot or multi-labeler setups.
- Workforce management - Work with multiple vendors? Manage multiple teams of annotators in a single interface.
Mindkosh offers a transparent pricing model where you only pay for the amount of time you spend labeling and nothing more! Checkout our pricing here.
Encord – Data-centric labeling platform
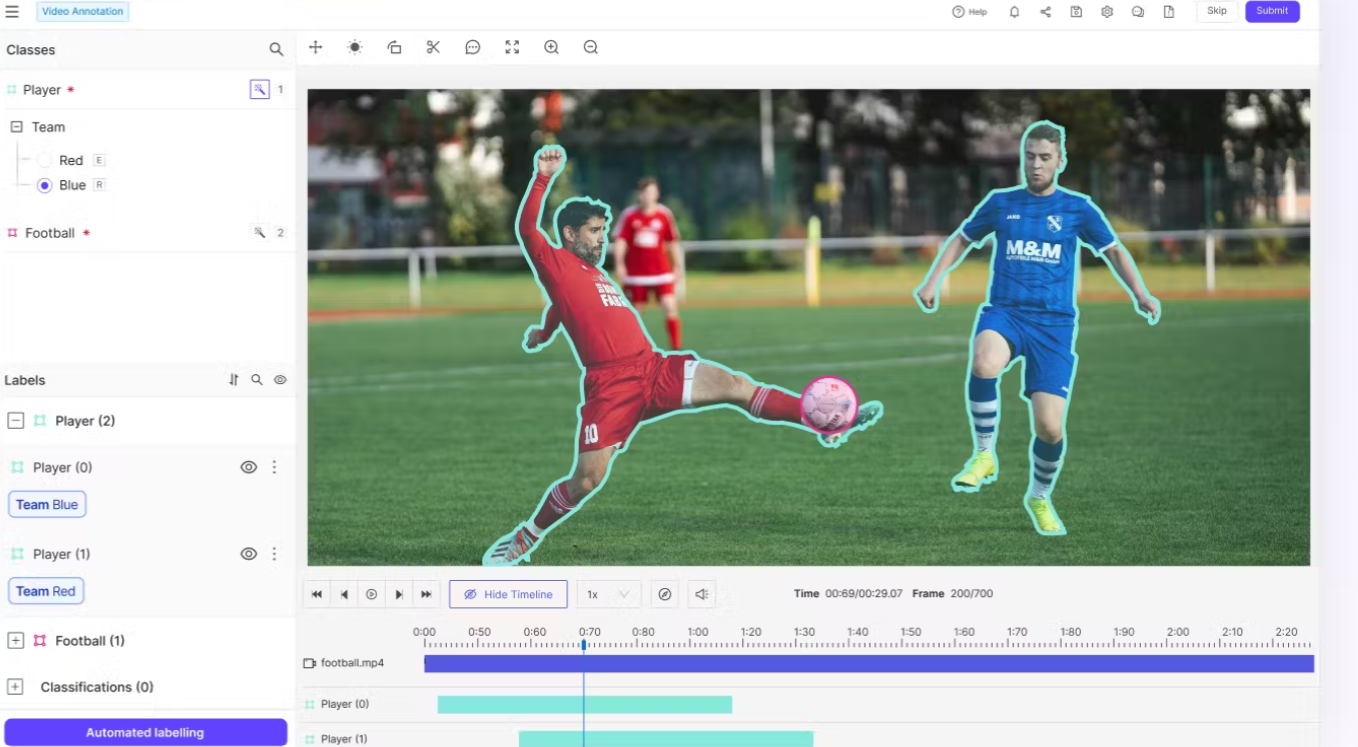
Encord positions itself as an enterprise-ready annotation platform with strong compliance features (SOC2, HIPAA) and audit trails. It provides structured, ontology-driven workflows and integrates with ML pipelines. It excels at 2D tasks but has lighter support for sensor fusion.
- Sensor Support: Limited LiDAR/radar support (in beta as of writing this article). No support for multiple cameras and single channel images.
- Workflow & QA: Flexible ontologies, strong automation, customizable workflows and Active Learning loops.
- Scalability: Works well for growing teams, especially in vision-heavy workflows.
- Workforce management: Can invite users and assign them different permission roles, but does not support team management for different teams.
- Industry Readiness: Favored by ML teams focusing on model improvement via data-centric iteration. Popular in healthcare and autonomous driving, where regulatory compliance is critical.
Best for: AI teams focused on 2D image/video annotation with automation-first workflows.
Kognic – Automotive-focused pipelines
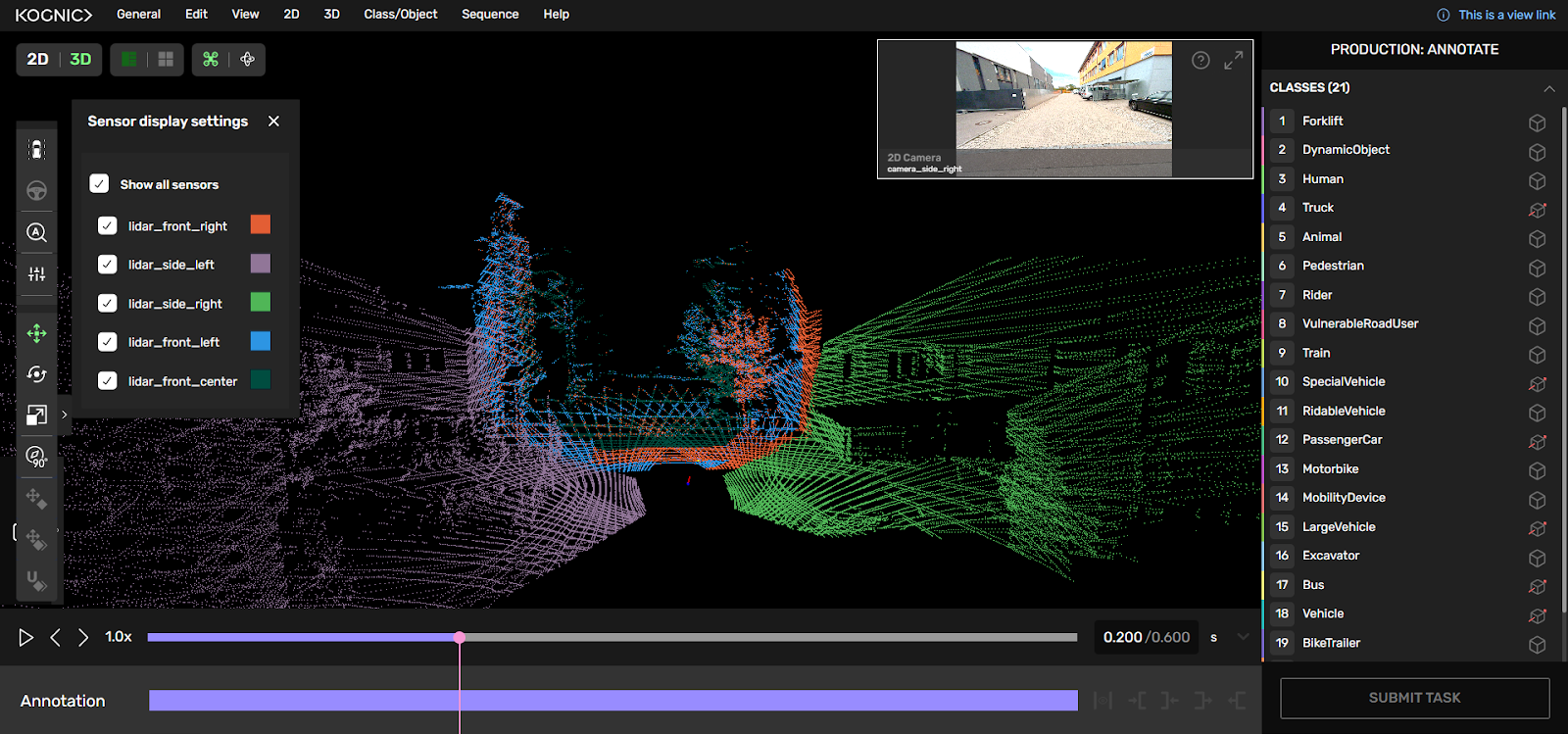
Kognic specializes in automotive-focused data pipelines. Built for OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers, it offers highly structured annotation and validation workflows tailored for safety-critical ADAS and AV applications. Kognic boasts a wide range of tools and features - which can sometimes make the workflow cumbersome and difficult to learn.
- Sensor Support: LiDAR, radar, multi-camera inputs.
- Sensor Fusion: Plenty of tools to help visualize annotations in all sensors, to enable Lidar sensor fusion annotation.
- Workflow & QA: Allow 3 workflow modes and have templates for basic checks like pedestrian height etc.
- Object Tracking: Allows tracking an object with consistent IDs, and automates the process a little through interpolation, and point cloud aggregation.
- Scalability: Designed for large-scale automotive datasets.
- Annotation export: Can export in Kognic's format for both point cloud and image annotations. However, no versioning is available.
- Workforce management: Kognic supports team management for managing multiple teams and assigning separate roles to each user.
Deepen AI – Calibration focused
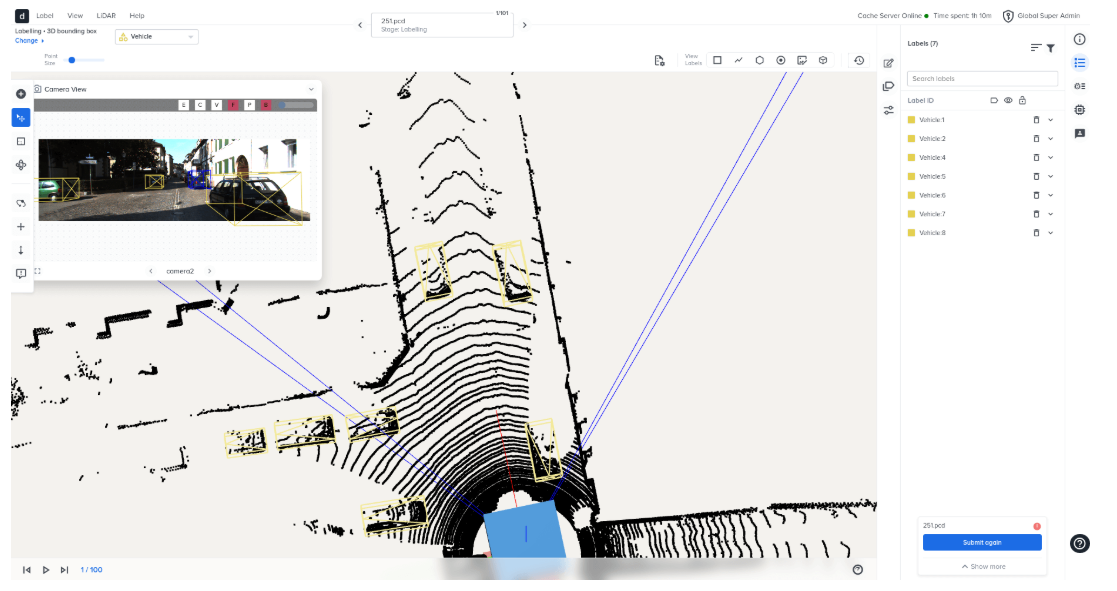
Deepen AI stands out for its expertise in calibration tools — a critical step in ensuring multi-sensor fusion accuracy. For annotation, while Deepen offers a good UI and a good set of features and tools necessary to label Lidar data, it does miss some key features like interpolation and static object labeling.
- Sensor Support: Support for LiDAR, camera and radar data.
- Sensor Fusion: Good support for multi-sensor calibration and alignment, one of Deepen's specialties.
- Workflow & QA: You can specify users for each phase of annotation (labeling, QA and final QA), however customization is not great. Limited support to perform QA and measure Annotation Quality.
- Object Tracking: Allows tracking objects through time and sensors, but lacks extensive features to make the process easier. Deepen does support point cloud Aggregation which is helpful.
- Annotation export: Can export in Deepen's format for both point cloud and image annotations. However, no versioning is available, and you can only export in the current state of the task.
- Workforce management: Deepen allows you to organize users into groups, but these are only used to assign permissions. No support for multiple team management.
CVAT – Open-source flexibility, very limited LIdar support
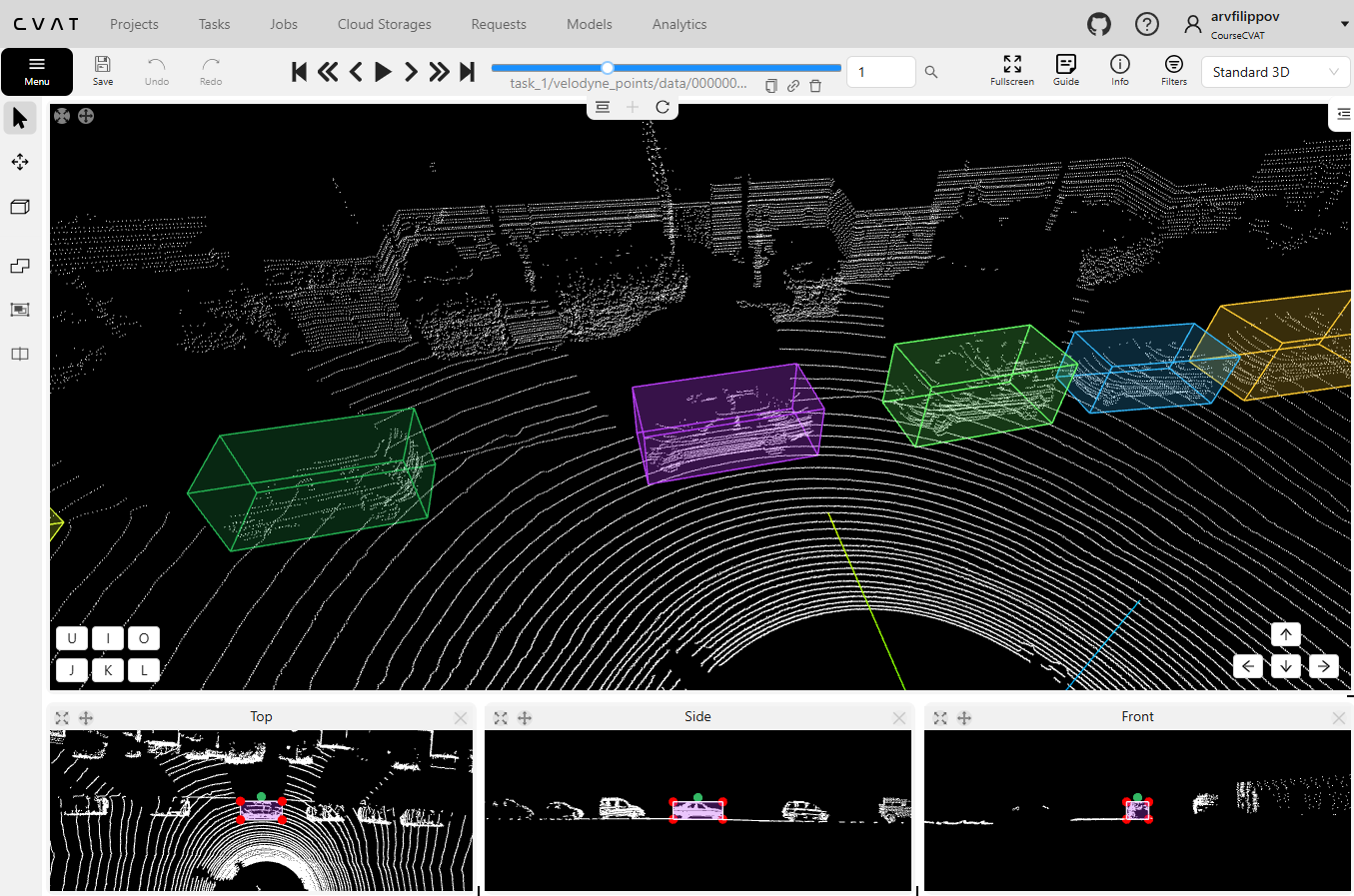
CVAT (Computer Vision Annotation Tool) is the most popular open-source annotation tool. It supports 2D and 3D annotation but Lidar annotation support is pretty basic, and setting it up requires some engineering effort. While CVAT might be OK for small scale Lidar annotation projects with limited scope, it is not suitable for production.
- Sensor Support: Limited Lidar support. Support adding reference images as well.
- Sensor Fusion: Does not support projection of Lidar annotations over images.
- Annotation tools: Limited Cuboid annotation only. Segmentation and polyline annotation is not supported.
- Workflow & QA: Fixed workflows and allows setting up a QC task that can be used to calculate Quality metrics for a project.
- Scalability: Self-hosted, with higher operational overhead.
- Industry Readiness: Popular in research labs and budget-conscious teams.
Best for: Research teams or startups with engineering resources to customize.
Scale AI – One of the first Lidar labeling tools
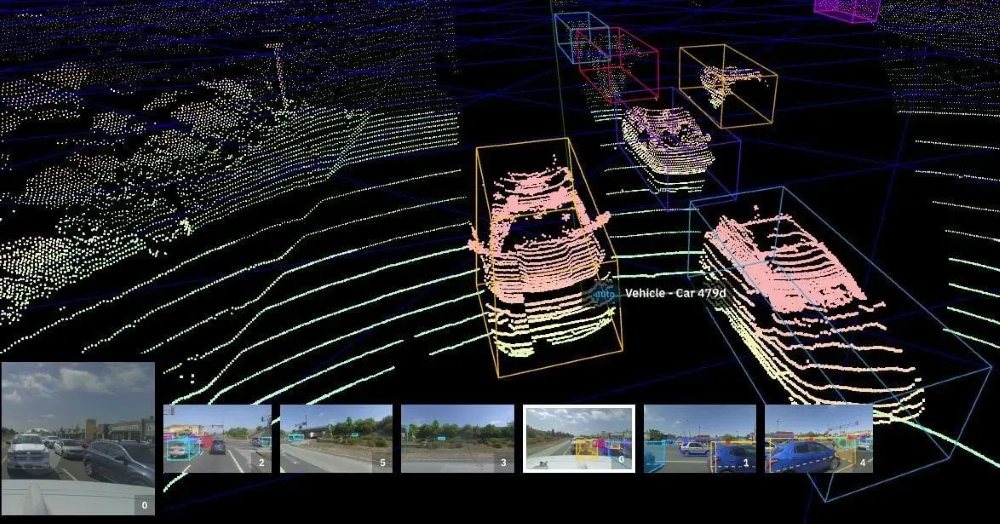
Scale AI is a well-known Data annotation solutions provider. While it is more widely known for its data labeling services, it also offers a Data annotation studio you can use with your own workforce. It was one of the first annotation tools with Lidar data support. However, Scale's annotation tool is designed very much for use with their own workforce, and might not be the best fit for teams looking to get their labeled by their own teams.
In recent times, Scale AI has also shifted their focus towards GenAI. In addition, their relationship with Meta has raised questions over data ownership and many large companies have reportedly severed ties with Scale for this reason.
- Sensor Support: Supports LiDAR, Radar, and cameras.
- Sensor Fusion: Multi-modal annotation supported, with projection over images.
- Workflow & QA: Combines automation with human-in-the-loop QC.
- Scalability: Very scalable, backed by enterprise deployments.
- Workforce management: Can invite users and assign roles, does not allow team management.
SuperAnnotate – UI-first labeling with outsourcing options
SuperAnnotate is optimized for 2D annotation with a strong interface and outsourcing marketplace, but lacks native LiDAR support.
- Sensor Support: Cameras only; No LiDAR/radar support.
- Workflow & QA: Customizable annotation workflows, but lacks extensive QA tools.
- Workforce management: Superannotate is built to work with external workforce and offers team management with ability to assign permissions to each user or team.
- Annotation export: Only supports Superannotate and COCO format support, but does not allow versioning of the annotation exports.
- Industry Readiness: Good for hybrid teams outsourcing part of their annotation.
Best for: Teams that need fast 2D labeling + outsourcing options, but not multi-sensor.
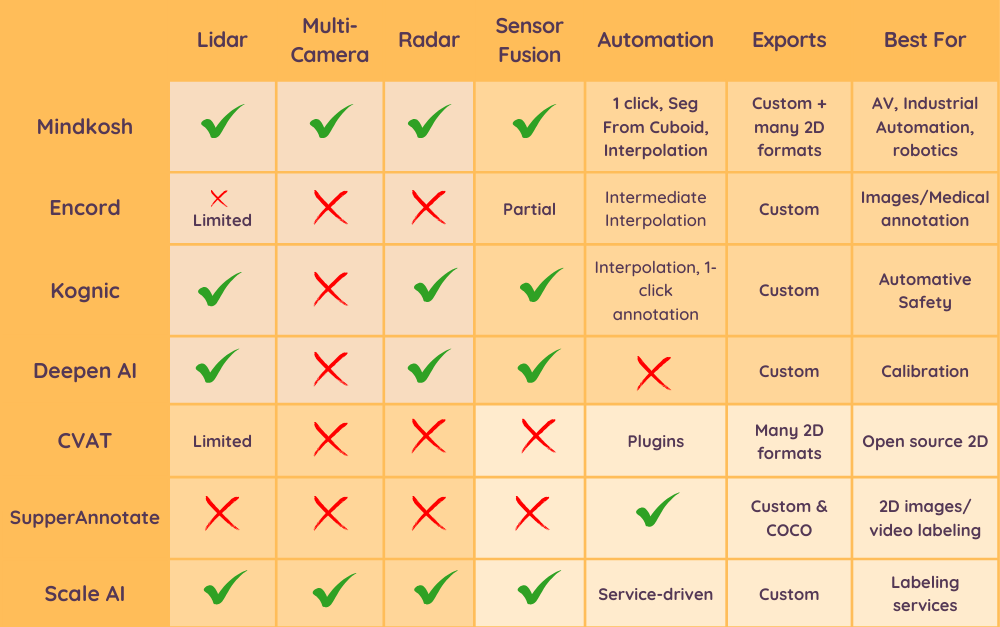
Conclusion
Choosing a sensor fusion annotation platform depends on your domain and scale:
- Mindkosh → Best for teams working on ADAS, Autonomous vehicles, Robotics and Industrial automation use-cases where Lidar sensor fusion or multiple cameras with single channel images (like depth and thermal camera images) need to be labeled.
- Kognic → Best of ADAS use cases that work with multiple Lidars. Can be daunting to train teams to use it due to the large number of overlapping tools.
- Deepen AI → Great for simpler ADAS use-cases, specially if calibration is needed.
- CVAT → Best for personal/hobby projects with only a few data points and no requirement of different annotation types.
- SuperAnnotate → Ideal for 2D image annotation with simpler needs.
- Scale AI → Teams looking to outsource their annotation needs.
- Encord → Solid for 2D data-centric annotation, but limited support for Lidar annotation.
For real-world sensor fusion challenges, only purpose-built platforms like Mindkosh deliver the right balance of automation, scalability, and precision.