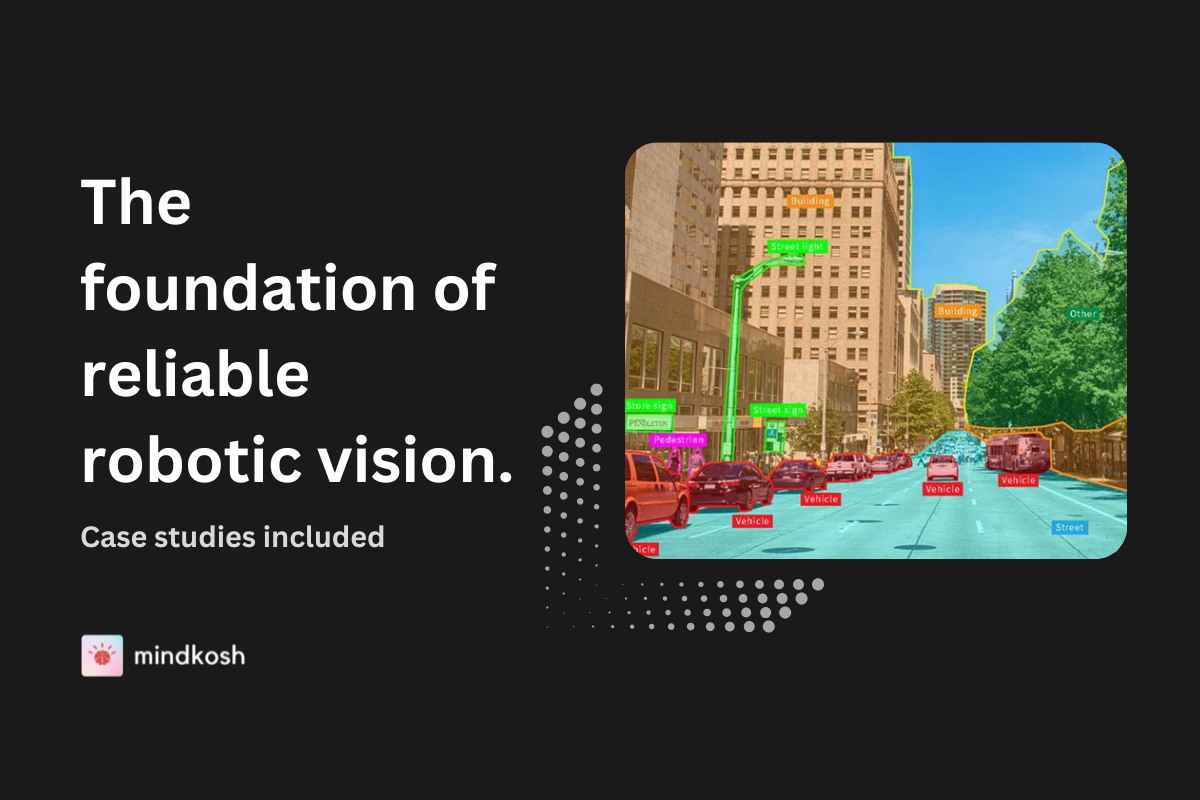
Every real-world AI team has felt the consequences of poor data: misclassifications that cause safety issues, personalization models that frustrate customers, and analytics pipelines that deliver misleading insights. Bad data doesn’t just hurt model accuracy—it drives up engineering costs, slows deployment, and damages trust.
Data-centric AI provides the solution by prioritizing clean, consistent, well-annotated data as the true driver of model performance.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved dramatically over the past few decades, moving from theoretical concepts to tangible, real-world applications that are reshaping industries. The focus has often been on developing sophisticated algorithms and models. However, there is a growing recognition that the quality, quantity, and management of data are equally, if not more, critical to the success of AI systems.
This shift toward a data-centric approach is redefining how we build reliable, high-performance AI systems. Below we talk about what Data centric AI means, why its important and how it impacts various industries. If you want to dive even deeper, check out our searchable list of research papers in Data Centric AI, and a list of publicly available tools.
Understanding data-centric AI
Data-centric AI emphasizes the importance of data over algorithms. In this approach, the primary focus is on improving the quality and relevance of data rather than just refining the algorithms. The rationale is straightforward: better data leads to better AI performance. The paradigm shift acknowledges that most AI systems, particularly those based on machine learning, are highly dependent upon the data they are trained on. High-quality data can significantly enhance model accuracy, robustness, and reliability.
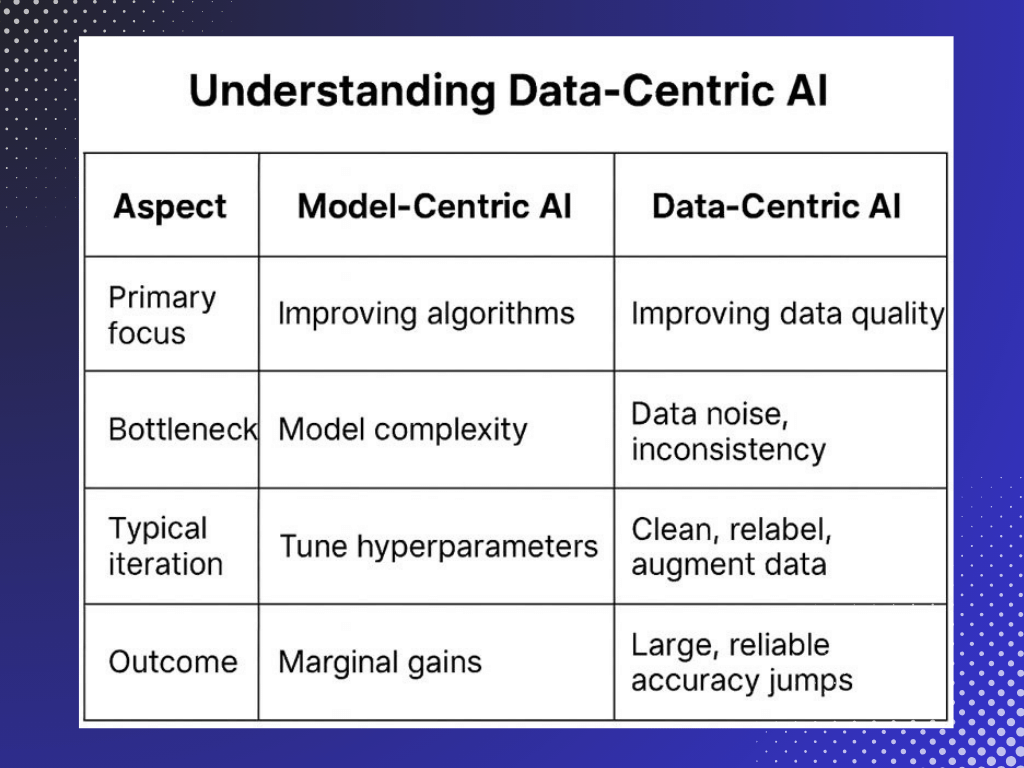
The Importance of data quality
High-quality data is the cornerstone of successful AI systems. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate models, faulty predictions, and ultimately, poor decision-making. Data quality encompasses several factors:
- Accuracy: Ensuring the data is correct and free from errors.
- Completeness: Making sure all necessary data points are included.
- Consistency: Maintaining uniformity in data format and structure.
- Timeliness: Using the most recent and relevant data.
- Relevance: Ensuring the data aligns with the problem being solved.
For example, in healthcare, AI models used for diagnosing diseases must be trained on accurate, comprehensive, and up-to-date patient data to provide reliable results.
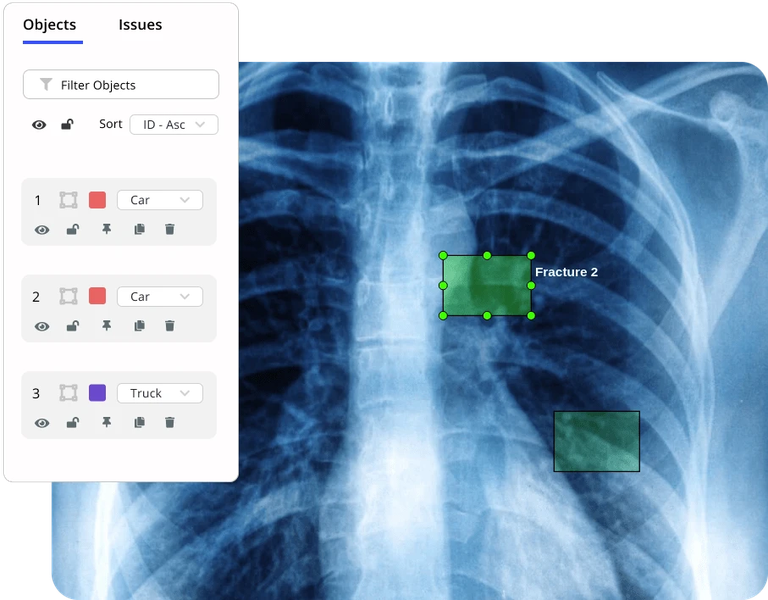
Data annotation and labeling
Data Annotation is a critical component of Data-centric AI, especially for systems that involve training supervised learning models. High-quality labeled data is essential for effectively training AI models. The process involves tagging data with relevant labels that help the AI system learn to recognize patterns and make predictions.
In applications such as image recognition, accurately labeling images is crucial. For instance, in autonomous driving, images of road signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles must be meticulously labeled to ensure the AI system can interpret and respond to its environment accurately.
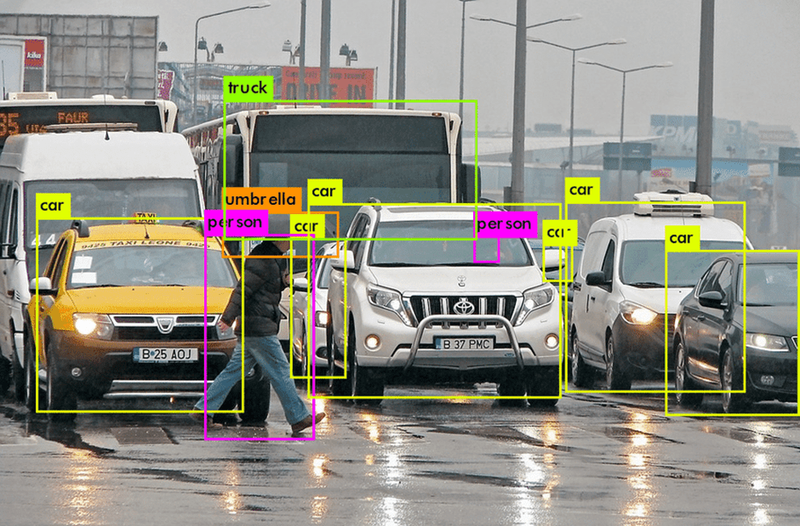
Data augmentation and enhancement
Data augmentation techniques can help overcome the limitations of small datasets by artificially increasing the amount of training data. These techniques involve creating new data points from existing ones through transformations such as rotation, scaling, and cropping in the case of images, or synonym replacement and paraphrasing in text data.
In industries like retail, data augmentation can enhance customer behavior models. By augmenting existing purchase data with synthetic transactions, retailers can train AI systems to predict customer preferences more effectively and enhance personalization.
Synthetic data in data-centric AI
Recent research further reinforces the value of data-centric AI, particularly the role of high-quality synthetic data in this context. DAViD (Data-Efficient and Accurate Vision Models from Synthetic Data) demonstrates that models trained on smaller, high-fidelity synthetic datasets can achieve the accuracy of much larger, computationally intensive models.
By using synthetic data with perfect labels and controlled diversity, the DAViD approach improves data efficiency while addressing challenges such as data privacy, usage rights, and bias. The results highlight a core principle of data-centric AI: better-designed data can deliver strong model performance at significantly lower cost.
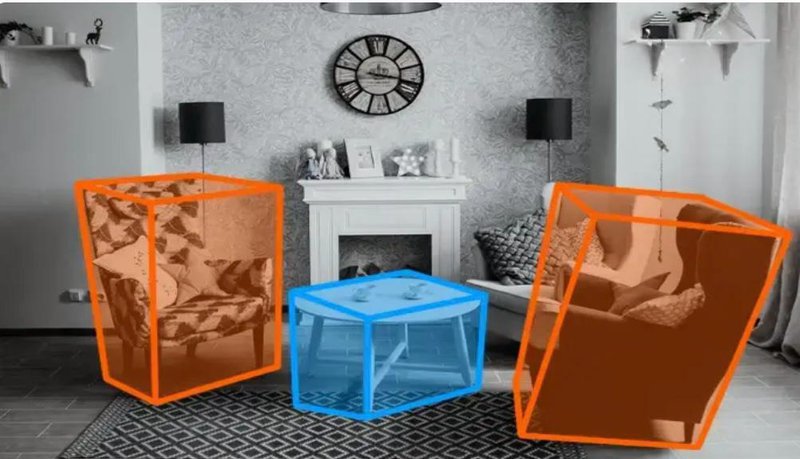

Real-world applications of data-centric AI
The impact of data-centric AI is evident across various industries. Here are some real-world applications:
Healthcare
In healthcare, data-centric AI is transforming diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient care. High-quality medical data, such as electronic health records (EHRs), imaging data, and genomic information, are crucial for training AI models. These models can then assist doctors in diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and helping personalize treatment plans.
For instance, AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze medical images to detect early signs of diseases like cancer with higher accuracy than traditional methods. Moreover, AI models trained on large datasets of patient records can identify patterns and predict complications, enabling proactive care.
Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on AI to navigate and make real-time decisions. The success of these systems depends on high-quality data from various sensors, including cameras, LiDAR, and radar. Data-centric AI ensures that these data sources are accurate, reliable, and well-integrated.
Annotated data play a significant role in training autonomous driving models. Detailed labeling of objects, road signs, and other elements in the environment is essential for the vehicle to understand and to respond appropriately. Continuous data collection and enhancement help improve the system's performance and safety over time.
Retail and E-Commerce
In the retail sector, data-centric AI is enhancing customer experiences and optimizing operations. By leveraging high-quality customer data, AI systems can personalize recommendations, predict demand, and optimize supply chains.
For example, e-commerce platforms use AI to analyze customer browsing and purchase history, enabling personalized product recommendations. Additionally, AI models trained on sales data can forecast demand, helping retailers manage inventory more efficiently and reduce costs.
Finance
The financial industry benefits from data-centric AI in areas such as fraud detection, risk assessment, and customer service. High-quality financial data, including transaction records and market data, are essential for training AI models that detect anomalies and predict risks.
AI-driven fraud detection systems analyze transaction patterns to identify suspicious activities in real time. Similarly, AI models used for credit scoring and risk assessment rely on accurate and comprehensive financial data to make informed decisions.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, data-centric AI is improving efficiency, quality control, and predictive maintenance. High-quality data from sensors, production logs, and maintenance records is crucial for training AI models that monitor equipment health, optimize production processes, and predict failures.
For example, AI-powered predictive maintenance systems analyze sensor data from machinery to detect early signs of wear and tear. This allows manufacturers to schedule maintenance proactively, reducing downtime and preventing costly breakdowns.
Challenges and future directions
Despite its potential, data-centric AI faces several challenges:
- Data Privacy: Ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive data is paramount, particularly in industries such as healthcare and finance.
- Bias and Fairness: Addressing biases in data to ensure fair and equitable AI outcomes remains a significant challenge.
- Data Integration: Integrating diverse data sources and ensuring their compatibility can be a complex and time-consuming process.
Looking ahead, advancements in data-centric AI are likely to focus on improving data annotation techniques, developing more effective data governance frameworks, and creating more sophisticated methods for handling biased and incomplete data.
Data-centric AI represents a paradigm shift in the development and deployment of AI systems. By prioritizing data quality, annotation, and governance, this approach improves the reliability, accuracy, and ethical standards of AI applications across various industries. As organizations continue to recognize the value of high-quality data, data-centric AI will play an increasingly pivotal role in solving real-world problems and driving innovation.